
Winding resistance test readings can check against factory-stated values. Winding resistance tests provide information about the condition of the windings. Predictive and preventive maintenance programmes which include regular testing can help detect winding issues early. While detecting problems in vital motors or generators is important, finding them before they lead to catastrophic failure is critical. The unit also features a visual and audible discharge indicator as a discharge condition occurs. The discharge function is passive and allows automatic discharge in the event of inadvertent power loss or if the test leads are accidentally disconnected. The MTO106 will automatically discharge this energy safely after a test is terminated. This energy must be dissipated safely from the winding after the test current is stopped.
#MOTOR WINDING RESISTANCE TEST GENERATOR#
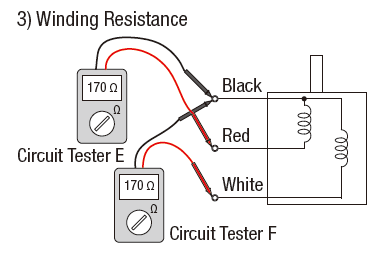
Motor or generator windings can store a large amount of energy when DC current is injected into them during the test (known as inductive charging). Safety is an important consideration when testing winding resistance. This eliminates the resistance of the lead set from the measurement, providing accuracy.

The winding resistance tester uses a four-wire measurement with a Kelvin lead set to improve measurement accuracy. Megger’s MTO106 provides up to 6 A of test current and 48 V of open circuit voltage. A regular multimeter cannot perform winding resistance measurements. 1: Phase-to-phase resistance measurement.Ī higher test voltage will overcome the inductance more quickly (up to 50 times faster than a normal low-resistance meter).

The tester must therefore safely inject sufficient test current at a more significant test voltage to measure the stator winding safely and timely.įig. However, the windings in large motors have low resistance and are very inductive. When applying DC test voltage, you should never exceed the voltage rating of the motor winding being tested.įor most common resistance measurements, you can use a regular multimeter set to the ohms (Ω) scale. Good insulation should have high resistance and typical values are in the MΩ or GΩ range. The tester then provides a resistance reading. Insulation resistance testers apply high DC voltage which causes a small current through the insulation being tested. One should not apply more than 10% of the winding current rating as this will warm the winding and create a changing resistance value as the copper or aluminum heats up.įor the electrical insulation component, an insulation resistance (IR) instrument is used to validate the condition of the winding relative to ground (outer case of the stator winding). Winding resistance testers apply a known DC current through the windings, measure the resulting voltage drop across the winding, and calculate the resistance. The mechanical condition and structure of the rotor or stator affects the winding resistance. Studies conducted by IEEE and the Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI) on electric rotating machinery failures show that 48% of motor failures are due to electrical failures.Īs with transformers, a motor or generator is broken down into two main components: insulation and mechanical. These problems include partial or fully shorted coils, poor crimps or connections, imbalance between phases (improper turns on phases) and incorrect coil (phasing) connections. Winding resistance measurements detect problems in motors which other tests may not find. Winding resistance measurements detect various faults in motors and transformers: shorted turns, loose connections, broken strands and malfunctioning tap changer mechanisms.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
